Introduction
In today’s digital age, data privacy and online security are growing concerns for users across the globe. With an increasing number of cyber threats, surveillance, and restrictions on internet content, it has become essential to find solutions that ensure safe and unrestricted access to the internet. One such tool is the Virtual Private Network VPN. This article provides a complete guide to understanding a virtual private network VPN explained in detail, from what it is and how it works to configuration, benefits, and legal aspects.
What Is a Virtual Private Network VPN?
A Virtual Private Network VPN is a service that creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet. It masks your IP address and routes your traffic through a secure server, protecting your data from hackers, internet service providers (ISPs), and third-party trackers. In essence, the virtual private network definition refers to the process of creating a private tunnel over the public internet. This tunnel ensures that all data traveling through it remains confidential and cannot be intercepted.

How Does a VPN Work?
Understanding how a VPN works can help you see its value. A VPN functions by encrypting your internet connection and routing it through a secure server located in a different region or country. This makes it appear as if you're browsing from that location. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how does a VPN work: Data Encryption: All your internet traffic is encrypted, making it unreadable to hackers or surveillance systems. IP Masking: Your real IP address is hidden and replaced with the IP of the VPN server. Secure Tunneling: A secure tunnel is created between your device and the VPN server, shielding your online activity from prying eyes. This process helps you stay anonymous and prevents websites from tracking your real identity or location.
Why Do You Need a VPN?
- Privacy Protection: Prevents your ISP or government from tracking your browsing habits.
- Secure Public Wi-Fi: Shields your data when using unsecured public networks.
- Bypass Geo-blocks: Access content restricted to certain countries, such as streaming services.
- Avoid Censorship: Enables access to blocked websites in countries with strict internet controls.
- Remote Work Security: Allows employees to securely access company networks from home or on the go.
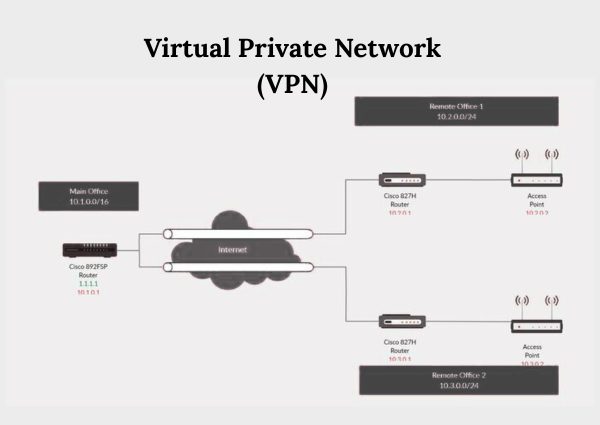
There are different types of VPNs tailored to various use cases. If you're wondering, What are the two types of VPN?, here’s a breakdown: This type of VPN allows users to connect to a private network from a remote location. It is commonly used by individuals or employees accessing internal company systems while working remotely. This VPN type connects two or more networks, such as company branch offices with the main headquarters. It's widely used in corporate settings to ensure safe communication between departments or branches. Personal VPN: Designed for individual users to ensure personal online privacy. Mobile VPN: Optimized for mobile devices, ensuring secure connections while on the move. Cloud VPN: Connects users to cloud infrastructure securely; often used by businesses.Types of VPN
1. Remote Access VPN
2. Site-to-Site VPN
Additional Types of VPN:
VPN Protocols: The Backbone of VPNs
VPN protocols determine how data is transmitted through the VPN tunnel. The 3 most common VPN protocols include:
- OpenVPN: Highly secure and open-source. Offers strong encryption and is widely supported.
- IKEv2/IPSec: Ideal for mobile users due to its ability to reconnect quickly after connection drops.
- L2TP/IPSec: Offers good encryption but can be slower. Still used in various legacy systems.
Each protocol offers different benefits in terms of speed, stability, and security.
How to Configure a VPN
Setting up a VPN is not as complicated as it may seem. Here’s how to VPN configuration works for most users:
Option 1: Using a VPN App
Choose a reliable VPN provider.
Download the app for your device.
Sign in and select a server location.
Click Connect and browse securely.
Option 2: Manual VPN Configuration
Windows: Go to Settings > Network & Internet > VPN > Add a VPN connection.
macOS: Navigate to System Preferences > Network > Add VPN configuration.
Mobile Devices: Use built-in settings or download VPN apps from Google Play or the App Store.
Router Setup: Configure VPN at the router level to protect all devices connected to your home network.
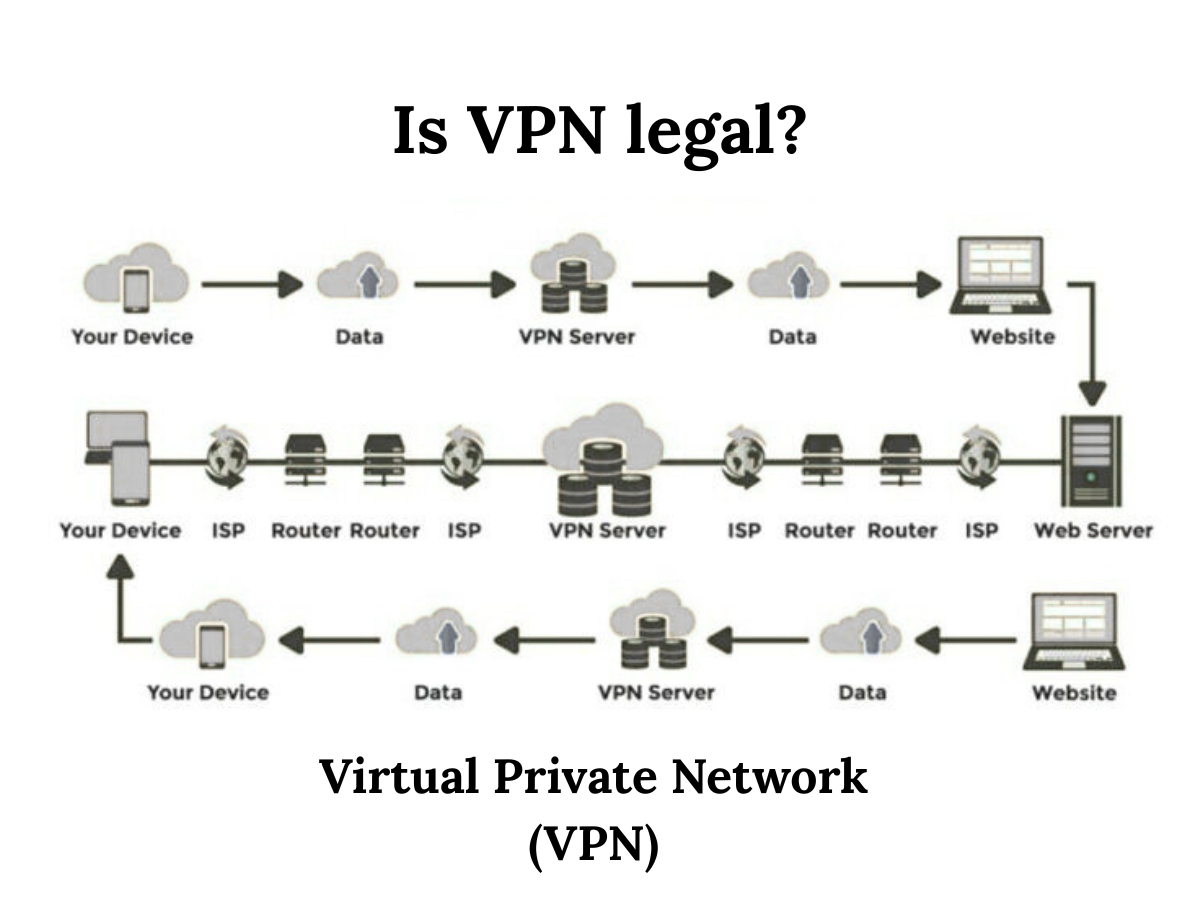
Is VPN Safe and Legal?
virtual private network VPNIs VPN safe? Yes, VPNs are generally safe when you use a reputable provider. Avoid free VPNs that may log your activity or sell your data.
Is VPN legal? In most countries, including the United States, the UK, and Bangladesh, using a VPN is completely legal. However, in certain countries like China, Russia, or North Korea, VPN usage may be restricted or monitored. Always check local laws.
Advantages of Using a VPN
There are several benefits to using a virtual private network:
- Enhanced online privacy and anonymity
- Protection against cyber threats and hackers
- Access to geo-blocked content and platforms
- Bypass government censorship
- Safe browsing on public Wi-Fi networks
Disadvantages of Using VPN
Despite the many benefits, there are a few downsides to consider:
- Reduced Speed: Encryption can slow down internet performance.
- Blocked Content: Some streaming services detect and block VPNs.
- Complex Setup: Manual configuration may be difficult for beginners.
- Trust Issues: Some VPN providers may log or misuse your data.
Who Uses VPN?
The range of virtual private network VPN users is vast and includes:
- Remote workers who need access to corporate data.
- Students accessing educational material from restricted areas.
- Travelers who want to watch content from home.
- Privacy advocates who prioritize anonymous browsing.
- Businesses ensure secure internal communication.
Real-Life Virtual Private Network Example
Consider this virtual private network example: You’re in Bangladesh but want to watch a movie available only on the US version of Netflix. With a virtual private network VPN, you connect to a US server, and Netflix sees you as a US user. You gain instant access to that region’s content.
This is just one example of how virtual private network VPN enhance your online experience.
Final Thoughts
In a digital world where data is the new currency, using a virtual private network VPN explained the right way is essential. From protecting personal data to unlocking the internet’s full potential, a virtual private network VPN is your ally in maintaining security and freedom online. Whether you’re a business professional, student, or everyday user, there’s never been a better time to start using a virtual private network VPN.virtual private network VPN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A VPN is a service that encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server to protect your privacy.
It encrypts your data and masks your IP address, making it difficult for third parties to track or intercept your activity.
A VPN provides encrypted connections over the internet, while a virtual network is typically a software-based LAN within a data center or cloud.
Main advantages include increased privacy, secure data transmission, and access to restricted content
OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPSec, and L2TP/IPSec.
VPNs are used by businesses, students, travelers, journalists, and privacy-focused individuals.
Yes, in most countries, but always verify based on your local laws.
Yes, especially when you use trusted providers that do not log your activity.
Potential slower internet speed, blocked content, and the need to trust your VPN provider.
